Multi-Tenant Learning Management Systems (LMS)
Advantages and Challenges in Overview
Multi-tenancy is a key feature of modern Learning Management Systems (LMS) that allows companies to manage multiple independent entities – such as departments, subsidiaries, or external partners – on a shared platform. However, before deciding on a multi-tenant LMS, it’s essential to understand the specific advantages and challenges of this architecture.
In this text, we will provide a detailed explanation of the advantages and disadvantages of multi-tenant LMS (vs single-tenant). You will gain a clear understanding of how such an architecture can support your organization and what challenges need to be considered.
Additionally, we will introduce a powerful Optimized Multi-Instance Solution that allows using the same LMS platform for different instances while employing strictly separate databases for maximum security and flexibility.
Discover how you can leverage the benefits of a centralized infrastructure without sacrificing individual customizations and security measures.
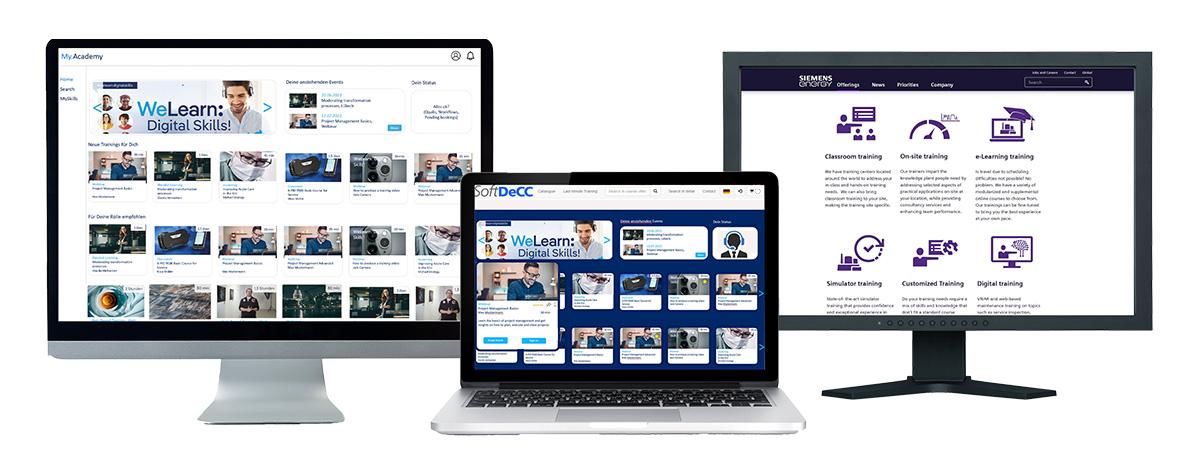
Advantages of a Multi-Tenant LMS
| Efficient Management & Central Control | A multi-tenant LMS enables companies to manage multiple training units or organizations on a single, centralized platform, significantly reducing administrative overhead. All tenants share the same infrastructure, which streamlines processes. |
Centralized updates, maintenance, and security measures need only to be performed once, reducing costs and effort for the IT department. This is especially advantageous for global companies with multiple locations and business units |
| Scalability and Flexibility | New tenants or training units can be added quickly without the need for separate installations, offering high scalability, which is particularly beneficial for expanding companies. |
Tenants can be customized individually, allowing each unit to manage its own learning content, user interface, and access rights while sharing the underlying infrastructure. This enables both company-wide and locally specific training needs to be efficiently met. |
| Cost Savings through Shared Resources | Shared resources such as servers, storage, and network capacity lead to significant cost savings. Particularly with large user bases and global distribution, a multi-tenant system can be more economical than separate installations due to optimized resource usage. |
A single license can often be used for multiple tenants, further reducing licensing costs. |
| Centralized Reporting and Analytics | A multi-tenant LMS enables data and reports to be aggregated across all tenants. Companies can generate centralized reports to measure the effectiveness and efficiency of their training programs across various business units. |
Centralized data analysis allows patterns and trends to be identified across the organization, contributing to the optimization of learning strategies. |
Challenges and Potential Drawbacks of Multi-Tenancy
| Security Complexity and Data Isolation | Sharing infrastructure increases the security requirements and the need for clear data isolation. A misconfiguration or security breach could potentially lead to data being accessible between tenants. |
In highly regulated industries (e.g., healthcare or finance), strict compliance requirements can present additional challenges. Companies must ensure that the LMS has robust data isolation and encryption mechanisms to meet these demands. |
| Limited Customization | While tenants can be customized, making deep changes to the system (e.g., specific feature extensions or custom integrations) is often more challenging. Since all tenants operate on the same codebase, customizations must be designed to ensure they don’t negatively impact other tenants. |
Companies with very specific LMS requirements may find that a multi-tenant system doesn’t offer the same flexibility as a fully dedicated installation. |
|
Performance and Scalability Risks |
In a multi-tenant architecture, all tenants share the same resources. If one tenant has particularly high demands or during peak usage times, resource competition can negatively impact performance for other tenants. |
Performance issues can be harder to diagnose, as all tenants operate on the same platform, and the system may respond differently under high load. Careful planning and resource allocation are therefore crucial. |
| Dependence on Centralized Administration | A multi-tenant LMS means that all tenants are dependent on the same centralized platform and administrative decisions. If problems or downtimes occur, all tenants are affected. With separate installations, an issue might be isolated to a single unit without affecting others. |
There’s also the risk that a centralized update or maintenance strategy may not always meet the specific needs of individual tenants. |
Optimized Multi-Instance Solution
An optimized Multi-Instance Solution between a fully multi-tenant architecture and completely separate installations involves running different instances of a Learning Management System (LMS) on the same infrastructure, but using separate databases for each instance.
This approach combines some of the benefits of multi-tenancy with the security and flexibility of separate installations.
Key Features of multi-instance Infrastructure
|
Shared Infrastructure, Separate Databases |
Technical Basis: All LMS instances run on the same server and software infrastructure but use separate databases for user data, course content, learners, course enrollments, reports, and analytics. |
This allows centralized management and shared server resources while ensuring that data remains fully isolated. Security risks associated with shared databases are significantly reduced. |
| Enhanced Security and Compliance |
Strict Data Isolation: Each instance accesses only its own database, meaning that there is no possibility of accessing data from other instances. This meets higher security requirements and simplifies compliance with data protection regulations and industry-specific standards. |
Independent Backups: Each database can be backed up and restored independently, minimizing the risk of data loss and optimizing data protection. |
|
Individual Customization per Instance |
Flexibility: Although the instances use the same software base, many aspects can be individually configured and customized without affecting other instances. This includes specific settings for user interfaces (training portals), roles, and access rights, as well as individual course offerings. |
Customized features and layout for various target audiences' requirements. |
| Central Management & Shared Resources |
Shared Maintenance and Updates: Since all instances are based on the same installation, software updates, security patches, and maintenance tasks can be performed centrally, reducing administrative effort compared to fully separate installations. |
Cost Savings: By sharing hardware and network resources, operational costs can be reduced compared to entirely separate installations. |
| Scalability and Performance |
Flexible Scaling: This solution offers a good balance between scalability and performance. The infrastructure can be centrally scaled, while each instance, operating with its own database, has independent performance. As needs grow, specific performance improvements can be targeted for individual instances without affecting the overall system. |
Resource Allocation: Careful resource planning ensures that peak loads in one instance do not impact the performance of other instances. |
| Potential Challenges |
Setup Complexity: Setting up and managing separate databases requires more effort than a purely multi-tenant solution. Configuring and operating multiple databases must be closely monitored to ensure that system resources are used efficiently. |
Cost Consideration: While shared infrastructure saves costs, the demands of separate databases and specific customizations for each instance may offset some of those savings. It’s important to carefully weigh the cost advantage. |
Conclusion
The discussion on the advantages and disadvantages of multi-tenant Learning Management Systems (LMS) clearly highlights that this architecture offers both significant benefits and challenges:
- A multi-tenant LMS enables significant cost savings through shared infrastructure and centralized management, which is particularly beneficial for large organizations with multiple business units. Additionally, it facilitates efficient scaling and centralized control.
- However, security concerns and limitations in individual customization can pose challenges, especially in highly regulated industries or when specific requirements of individual departments need to be addressed.
TCmanager® utilizes an optimized LMS solution that is based on a single LMS installation but uses separate databases for each instance.
This architecture combines the benefits of a centralized infrastructure - such as efficiency and cost advantages through centralized management - with the security and flexibility of isolated databases.
Thanks to this strict data isolation, companies can meet critical compliance requirements, such as GDPR or industry-specific security standards, while also making individual customizations for each instance.
In this way, TCmanager® offers an ideal balance, achieving many of the advantages of a true multi-tenant LMS without its complexity and potential limitations.
Advantages Multi-Instance LMS Solution
• Enterprise-Level Security: Separate databases ensure complete data isolation and compliance (e.g., GDPR, ISO 27001).
• Maximum Flexibility: Each instance can be configured individually and tailored to specific requirements, without affecting other instances.
• Centralized Administration & Minimal Maintenance: Updates, patches, and maintenance are handled centrally, reducing effort and costs.
• Scalability and Performance: New tenants or business units can be added quickly and resource-efficiently without impacting the overall system.
• Cost Efficiency: Shared infrastructure and licensing significantly lower operational costs.
FAQs on Multi-Tenant LMS
What is a multi-tenant LMS?
A multi-tenant LMS is a learning platform that manages multiple independent organizational units (tenants) on a shared software base. Each tenant has its own users, content, and settings, all centrally administered.
What are the benefits of a multi-tenant LMS for companies?
Multi-tenant LMSs provide cost efficiency through centralized infrastructure, scalability, individual customization for each tenant, and centralized reporting across all units. This allows training processes to be managed flexibly and transparently.
What is the multi-instance architecture as an alternative to a true multi-tenant LMS?
Many modern solutions, such as TCmanager®, use an optimized multi-instance architecture: a single LMS installation employs separate databases for each tenant instance. This approach combines the advantages of centralized management - efficiency and cost savings - with the security and flexibility of isolated databases. Compliance requirements are met, and individual customizations per tenant are possible.
Why is the multi-instance architecture often a better choice than a true multi-tenant LMS?
The multi-instance solution provides better data isolation, enhancing data security and compliance. At the same time, it reduces complexity in updates and maintenance compared to separate individual installations. Companies thus benefit from high flexibility and stability with manageable effort.
Which companies are suited for a multi-tenant LMS or multi-instance system?
Large, internationally operating companies, training centers, and corporations with multiple subsidiaries or external partners particularly benefit from multi-tenant LMS and multi-instance systems. These solutions enable centralized management while maintaining individualized learning environments.
How does TCmanager® as an example of a multi-instance LMS support companies?
TCmanager® uses a multi-instance architecture, where a single LMS installation employs separate databases for each instance. This ensures secure data isolation, flexible tenant-specific customizations, and centralized administration. TCmanager® is therefore ideal for companies seeking to combine scalability, compliance, and tailored learning processes.
How does a multi-tenant or multi-instance LMS scale with growing demand?
Multi-tenant and multi-instance LMSs are highly scalable, as new tenants or instances can be added easily without additional software installations. This enables rapid growth and resource-efficient use of infrastructure.
Call us for your free Consultancy
We will be happy to share our experience with you.
Call +49 (0)89 / 3090 839 30 to arrange for your free Consultancy Appointment.
.webp)




