Smart Qualification: Leveraging Data and AI for Strategic Workforce Development
LEARNTEC: 6. 5. 2025 by Martin Knapp
The presentation “Skills, AI & Data – The Future of Qualification?” by Martin Knapp at LEARNTEC 2025 highlights how companies can elevate their qualification management through the strategic use of data, dashboards, and artificial intelligence (AI).
The focus lies on data-driven decision-making, strategic transparency, and the ability to manage training initiatives more individually. The presentation emphasizes that AI can only reach its full potential when a structured and analyzable data foundation is in place.
The presentation is divided into four main areas:
- Typical Starting Point & Goal
Many companies have clearly defined goals and a comprehensive training portfolio. However, participation rates—especially for voluntary trainings—often fall short of expectations. - From Competency Matrix to Qualification Profile:
It explains how companies can use competency matrices to develop individual qualification profiles in order to plan targeted development measures. - Standardized Evaluations Using Dashboards:
Dashboards enable transparent and efficient analysis of training data, allowing informed decision-making. - How Can AI help?
AI can assist in identifying skill gaps early, analyzing future learning needs, and prioritizing strategic development areas.
In summary, the presentation demonstrates that the successful integration of AI into qualification management requires a solid data foundation. Only through structured collection and analysis of relevant information can companies unlock AI’s full potential to strategically and individually shape employee development.
About Martin Knapp
Focused on creating modern learning technology environments, promoting product innovation and AI, and expanding strategic partnerships.
13 years of experience in industrial environments:
- Internal IT consulting & project portfolio management
- Team leadership in training design & development – internal full-service provider: consulting, eLearning content creation, trainers, LMS
- LMS, training, and reporting strategies including implementation, metric definition, and goal achievement (quality & quantity)
- Expansion of qualification management in production environments
- LMS expansion project management
- Establishment and expansion of a reporting landscape for complex training analytics & progress reports
- Piloting innovations in simulation & augmented reality
Typical Organizational Starting Point: Training Programs and Their Effectiveness
In many organizations, business success is clearly defined and measurable – for example, in terms of growth metrics, efficiency gains, or quality targets. To systematically support this success, companies establish a portfolio of training and qualification programs that include both mandatory and voluntary learning opportunities for employees.
Ideally, these training programs contribute directly to the achievement of business goals: employees complete the courses fully and on time, apply the acquired knowledge effectively, and thereby enhance their job performance. In this way, training initiatives are intended not only to foster individual competencies but also to make a measurable impact on organizational success.
However, reality often paints a different picture. Participation rates in voluntary training programs are typically moderate at best. Even for mandatory courses, completion rates frequently fall short of expectations – which in turn limits the overall impact of learning initiatives on business outcomes.
So how can this issue be addressed? How can organizations – especially large and complex ones – identify obstacles and implement targeted measures to increase the effectiveness of their training programs?
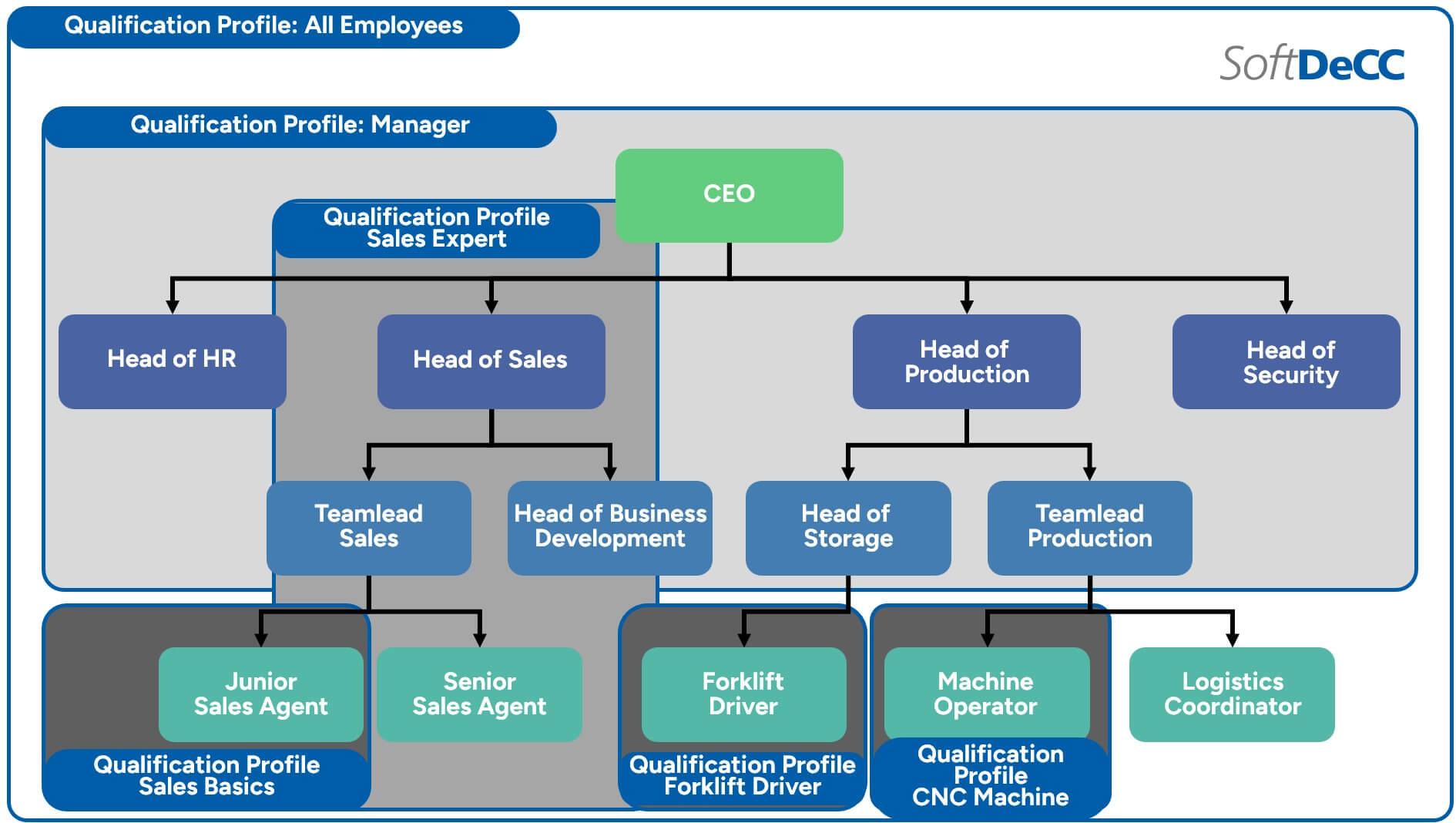
A good starting point is to examine the classical hierarchical structure of many companies. These are often organized by functional areas such as production, sales, or administration, and divided into multiple management levels.
Within such structures, a detailed analysis can help uncover the root causes of low participation rates and discover tailored solutions.
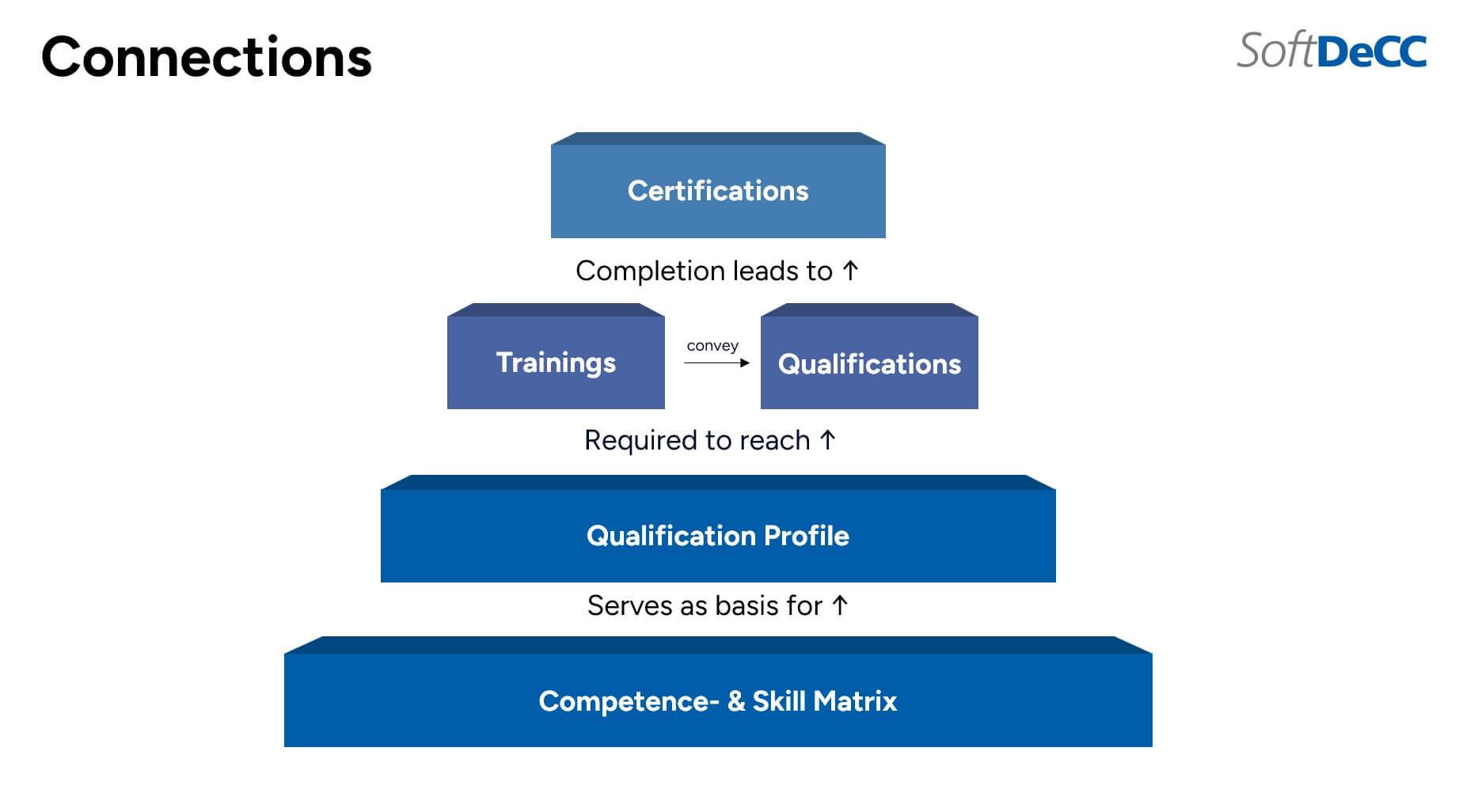
Clear Data Structures – Basis for Targeted Qualification Projects
From Organizational Chart to Competency Matrix: The Path to Structured Qualification Management
A closer look at the company’s organizational structure reveals a clear truth: different departments and hierarchy levels require distinct qualifications and competencies. The expectations for a production manager differ fundamentally from those for a junior sales employee or a legal professional. To plan and manage training initiatives effectively, a structured approach to qualification management is essential.
The core idea is to develop qualification profiles for each division, department, leadership level, and ultimately for every individual position. These profiles define the knowledge, skills, and competencies required to successfully fulfill each role.
To support this process, competency matrices are used to capture both shared requirements across similar roles and specific qualifications unique to individual positions. For example, a general set of competencies might apply to all managers, while additional criteria are tailored to the specific needs of production or sales leadership roles.
At this point, the use of a flexible software system becomes crucial. The system must enable modular and customizable assembly of qualification requirements into individual competency profiles. It should also recognize alternative qualifications as equivalent, allowing them to fulfill the same requirement. In other words, for a given competency, either Qualification A or Qualification B may be acceptable – providing much-needed flexibility for diverse career paths, prior experience, and alternative learning achievements.
Additionally, the system must account for differences based on location or country-specific regulations. For instance, safety standards at a production site may vary significantly depending on local laws and requirements. A modern qualification management solution should automatically incorporate such context-specific differences to ensure that the competency profiles remain accurate, complete, and relevant across the organization.
From Administration to Strategic Steering:
What Questions Should Qualification Software Be Able to Answer?
Structured qualification management goes far beyond simply recording requirements and completed trainings. The real value emerges when data is systematically analyzed and delivered in a format that supports targeted decisions and actions. Qualification software thus becomes more than a tool for administration—it evolves into a strategic enabler for workforce development.
Different user groups need tailored insights and answers, presented with the right level of detail and clarity:
For HR / Learning & Development (L&D): Strategic Oversight and Portfolio Optimization
- What is the current qualification fulfillment level across the organization?
- Which departments or business units show particularly low compliance or qualification completion rates?
- How can we increase the overall qualification level—e.g., through new learning formats or structured campaigns?
- Which training programs are missing from our current portfolio to meet key requirements?
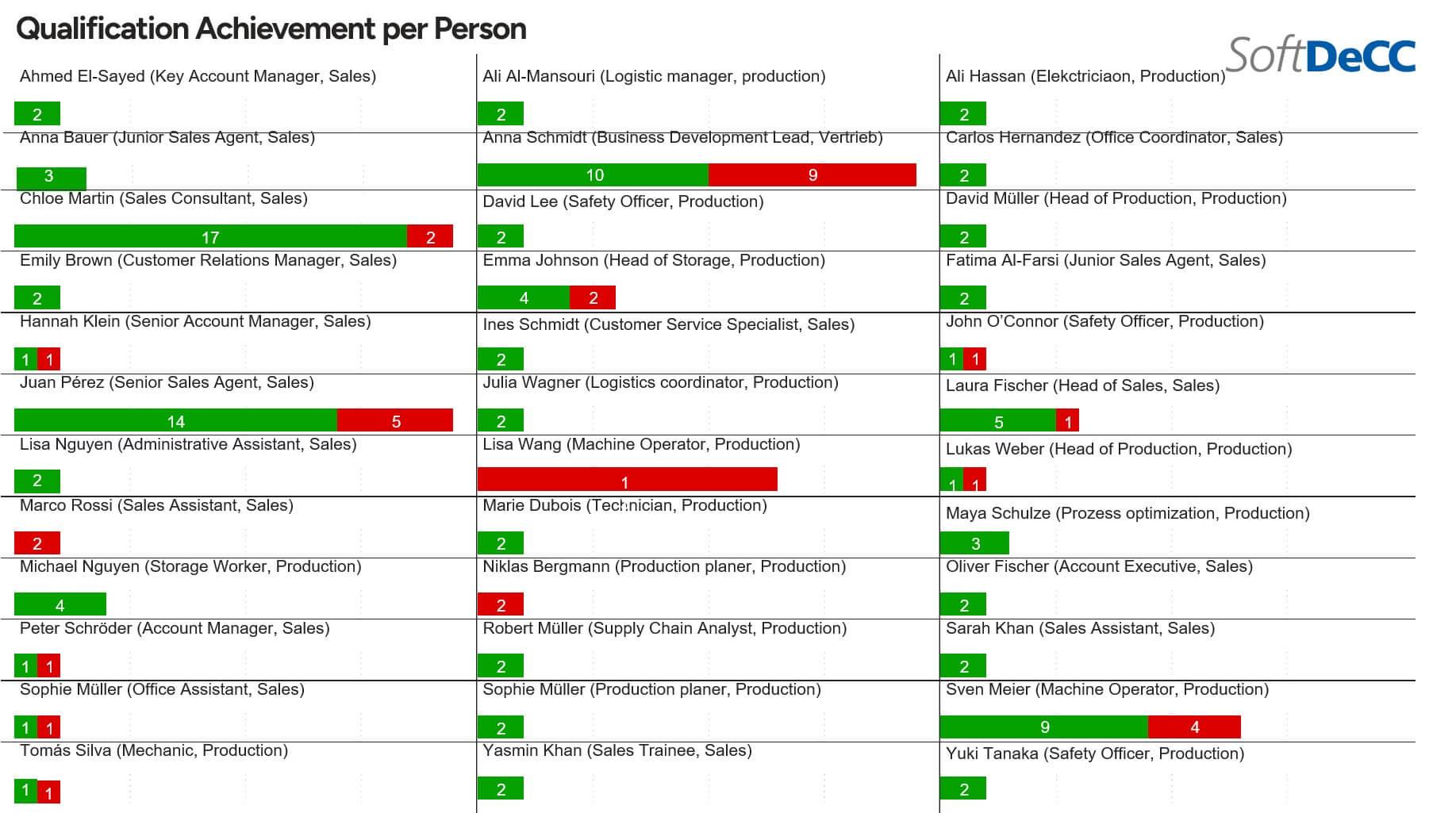
- Are there employees with significantly more or fewer trainings than expected—and why?
- What statistical insights can guide our planning?
– Percentage of employees who have completed all mandatory training
– Fulfillment rates by department, location, or business unit
– Trends in qualification completion over time
From Overview to Detail: Drill-Down to the Individual Employee Level
Especially for HR and Learning & Development teams, it is essential not only to view aggregated metrics, but also to drill down into detailed data when necessary. A robust qualification management system must therefore enable employee-level analysis.
Such drill-down capabilities make it possible to pinpoint individual employees with unusually low qualification fulfillment—relative to their peers or to the expectations of their role. This level of detail is critical for investigating root causes and addressing them effectively.
Often, what appears at first glance to be a deficit turns out to have a valid explanation: the individual may have only recently joined the company, the relevant course may not yet be available, or a personalized development plan may already be in place. Only with this contextual understanding can appropriate and fair actions be taken.
In this way, qualification tracking becomes more than just compliance monitoring—it becomes a constructive tool for steering development, focusing on insight and support rather than mere evaluation.
For Managers: Operational Oversight and Team Responsibility
- What is the current qualification status of my team?
- Are there team members who haven’t completed their mandatory trainings yet?
- Do I need to follow up or remind anyone to complete outstanding training?
- Which training programs can I recommend to a specific team member, based on their role, potential, or upcoming tasks?
For Employees: Transparency, Guidance, and Career Development
- How complete is my current qualification profile?
- Which requirements have I already fulfilled, and which ones are still pending?
- Are there specific training recommendations for me to complete next?
- Which learning opportunities could help me grow professionally—either in my current role or with a view toward future career goals?
Transparency as the Key to Action
Only with full transparency into qualifications, requirements, and development status can organizations gain meaningful insights. When it becomes clear where skill gaps exist, who requires action, and which measures are most effective, strategic decisions can be made with confidence.
A smart qualification management system provides the foundation to move from reactive administration to proactive workforce development—driven by data, aligned with goals, and focused on long-term success.

Multi-Level Access to Information: From System Reports to Personal Development Dialogues
To ensure that transparency is not just theoretical but actively contributes to day-to-day operations, qualification-related information must be made available across multiple levels and channels—tailored to the roles and needs of different user groups.
- The Learning Management System (LMS) serves as a central platform for this purpose. It provides access to analytics, reports, and statistics—filtered by permission levels, allowing HR or L&D professionals broader access than individual managers or employees. In addition, managers and learners benefit from dedicated functions within the learning portal that provide clear overviews of qualification statuses and recommended actions.
- Automated system emails—such as reminders about expiring or outstanding qualifications—ensure that important deadlines are not overlooked and that users are prompted to take timely action.
- Beyond digital channels, personal interaction remains a vital component of effective qualification management. In development discussions between employees and their managers or HR representatives, individual requirements, strengths, and career perspectives can be discussed in depth and translated into concrete learning paths.
This creates a holistic system in which information is not only accessible, but also actively used—to support individual growth and organizational success.
AI-Supported Insights: Beyond Dashboards and Basic Reporting
Modern qualification management systems increasingly integrate Artificial Intelligence (AI) to move from passive data visualization to active insight generation. Especially for HR, Learning & Development teams, or Corporate Academies, AI opens new opportunities for pattern recognition and strategic intervention.AI can automatically analyze all qualification profiles across departments and hierarchy levels to uncover anomalies, risks, and potential development needs.

For Staff Development & Academy
Here are some illustrative examples of findings that AI might surface:
- Leadership Development:
A very small target group is served by a broad and strategically important training portfolio. This discrepancy may indicate a potential bottleneck in succession planning or an underdeveloped leadership pipeline. - Machine Operators:
A high density of technical training requirements (e.g., 10 trainings for 2 individuals) presents a risk of knowledge silos. If even one person is absent or leaves the company, critical expertise could be lost. - Production Techniques:
No current demand is registered. This raises the question of whether courses should be removed or the target group redefined. - Sales Experts:
A highly demanding and diverse training program suggests a clear investment in high-potential employees, which can be strategic but should be monitored for scalability and inclusiveness. - Mandatory Trainings:
These are required company-wide by law or policy. High completion rates are critical, and AI can ensure ongoing compliance monitoring, flagging gaps automatically.
By continuously interpreting qualification data in context, AI helps focus attention where it matters most—supporting resource allocation, uncovering hidden risks, and enabling proactive talent development.
AI Support – Leadership Perspective
Leaders also benefit significantly when the qualification management system not only provides data but actively supports interpretation through the use of artificial intelligence. Rather than simply viewing dashboards, AI can help derive concrete recommendations for action—enabling proactive development, early risk detection, and targeted interventions.

Here are some practical application examples for leaders:
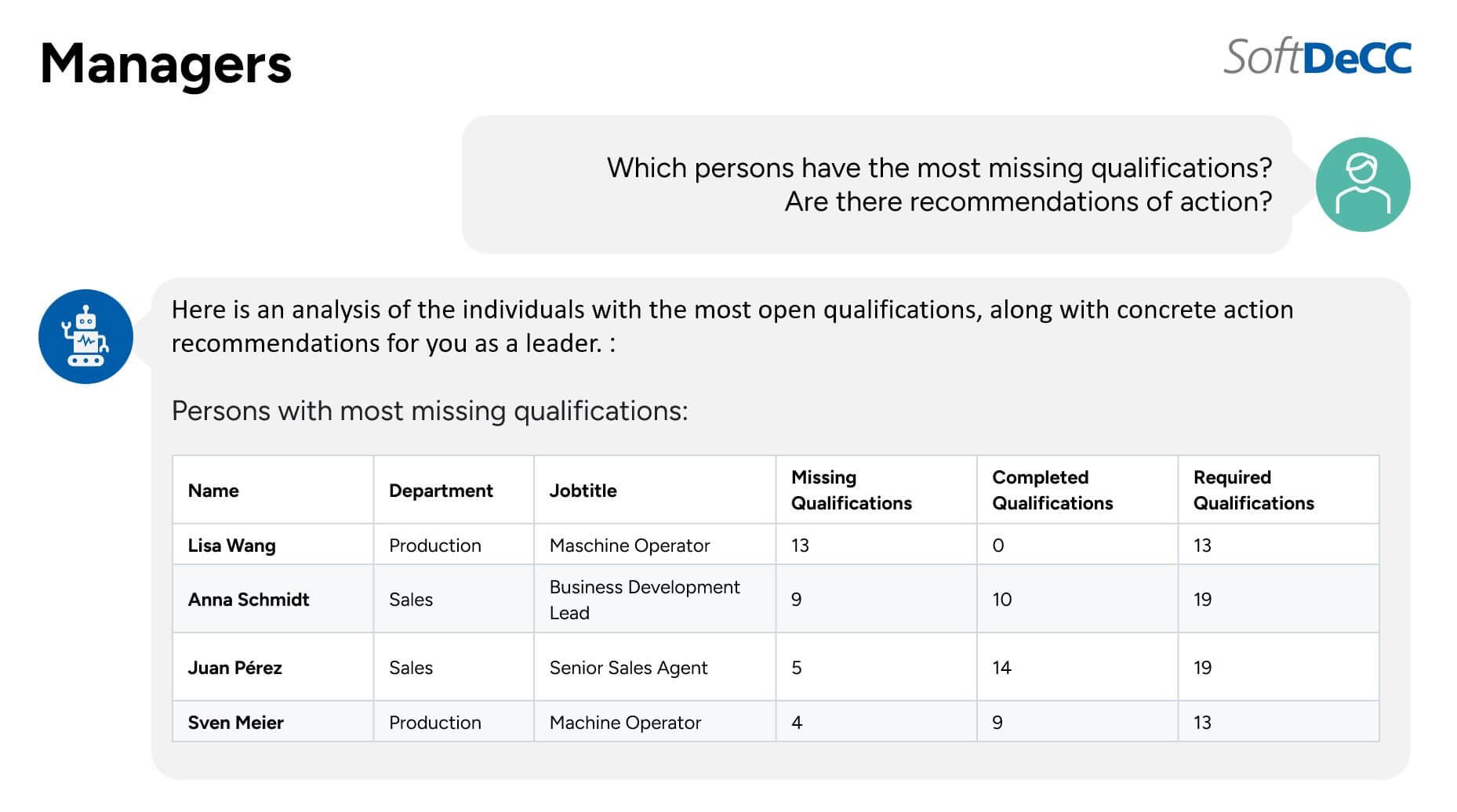
- Analysis & Prioritization:
AI highlights employees with unusually large qualification gaps and prioritizes where action is needed. - Define immediate actions:
Such as assigning urgent training, setting personal development goals, or focusing on critical competencies. - Understand and resolve root causes:
Through one-on-one conversations, managers can clarify whether missing qualifications are due to structural issues, lack of training availability, time constraints, or other factors. - Create individualized development plans:
AI suggests tailored learning paths with specific goals, deadlines, and responsibilities for each employee with significant gaps. - Encourage knowledge transfer:
Recommendations might include pairing less experienced employees with mentors or senior colleagues to speed up development. - Support regular monitoring and feedback:
Progress can be tracked through automated alerts, progress reports, and smart suggestions for follow-up actions. - Enable effective resource planning:
AI insights can reveal training bottlenecks or optimal scheduling windows to better integrate learning into everyday operations.
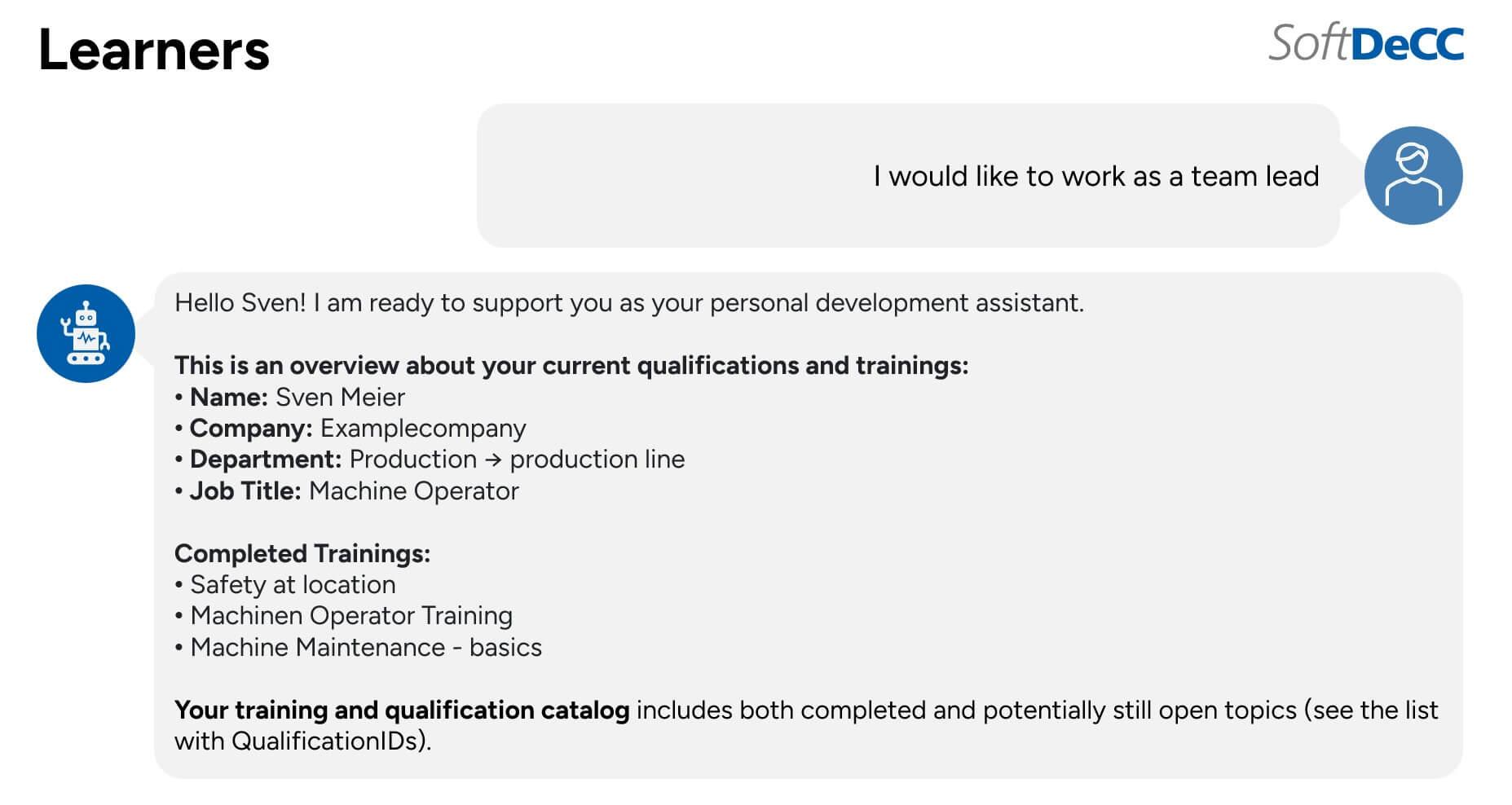
AI-Powered Learner Support: Personal Development Through Dialogue
One particularly effective way to support employees is by integrating an AI-powered chatbot that can respond to individual questions about qualifications and career development—available 24/7 within the learning platform.Instead of searching through training catalogs or course lists, the employee simply states their development goal.
For Example:
Instead of searching through catalogs or training overviews for a long time, the employee can formulate their goal – for example:
"I work in manufacturing and would like to take on a team leader position in the medium term – what do I need to do for that?"
The chatbot automatically analyzes:
- the employee’s completed trainings and qualifications,
- the requirements for the desired position,
- relevant available learning opportunities,
- and company guidelines for internal career advancement.
Based on this analysis, it provides:
- Personalized recommendations and prioritization of upcoming trainings or qualifications
- Suggested development paths based on the employee’s current role
- A clear overview of required vs. completed qualifications (e.g., in PDF or table format for use in development conversations)
- Reminders for recurring mandatory training, such as annual safety instructions
- Guidance on how to apply for further training opportunities
- Advice on continuing education in specific domains like machine operation or manufacturing
- Support in preparing for development discussions with managers
This interactive, data-driven dialogue empowers employees to take an active role in shaping their learning and career paths—quickly, easily, and with tailored guidance.
Choose your Systems with Technological Foresight
Systems That Scale and Unlock Strategic Value from Data
- Most companies have clearly defined goals and a comprehensive training portfolio to support them. However, participation rates, especially for voluntary trainings, often fall short of expectations.
- Companies can use competency matrices to create individual qualification profiles and to plan and communicate targeted development measures. In addition to HR development, the involvement of both managers and employees is essential.
- Standardized evaluations through dashboards enable transparent and efficient analysis of training data, supporting well-informed decision-making.
- Artificial Intelligence can help identify skill gaps early, analyze future learning needs, and prioritize strategic development areas.
Key Take-Away: The successful use of AI in the context of qualification requires a solid data foundation. Only through the structured collection and analysis of relevant data can companies harness the full potential of AI in qualification management to strategically and sustainably guide employee development.





